01. Types by Location
Mesothelioma Types by Location
Mesothelioma has four main types based on where tumors grow in the body. Mesothelioma occurs in the linings around the lungs, abdomen, heart and testicles. Mesothelioma can be further classified by cell type. The three main mesothelioma cancer cell types are epithelioid, sarcomatoid and biphasic.
Pleural Mesothelioma (Lungs)
Pleural mesothelioma forms in the lining around the lungs, also called the pleura. It accounts for 80% – 90% of cases, making it the most common type of mesothelioma. This rare cancer is caused by asbestos exposure. When a person inhales asbestos fibers, the fibers may end up in the pleura. Over time, irritation caused by these fibers may lead to tumor growth.
The median survival for pleural mesothelioma is about 18 months with treatment. Common pleural mesothelioma treatments include:
- Chemotherapy
- Extrapleural pneumonectomy (EPP) surgery
- Immunotherapy
- Pleurectomy decortication (P/D) surgery
- Radiation therapy
Doctors may combine treatments, a method called multimodal therapy. Combination plans are associated with better pleural mesothelioma survival than single treatment plans. For example, one study reported a median survival of 35 months in patients treated with chemotherapy plus surgery.
Peritoneal Mesothelioma (Abdomen)
Peritoneal mesothelioma forms in the lining of the abdomen, also called the peritoneum. This mesothelioma type accounts for 10% – 15% of cases. It is caused by asbestos exposure. When inhaled or ingested, asbestos fibers end up in the peritoneum. These fibers can cause irritation and cellular damage that can lead to tumor growth.
Median survival for peritoneal patients who receive treatment is about 2.5 years. Peritoneal mesothelioma patients have different treatment options, including:
- Chemotherapy
- Cytoreductive surgery (CRS)
Mesothelioma doctors may combine therapies for more effective treatment. For example, CRS plus heated intraperitoneal chemotherapy (HIPEC) are standard for qualified patients. HIPEC is a local chemotherapy applied to the abdominal cavity. Survival for patients who receive CRS and HIPEC may range from 2.5 to 7.5 years.
Pericardial Mesothelioma (Heart)
Pericardial mesothelioma forms in the lining of the heart, also called the pericardium. It is a rare type of mesothelioma, accounting for less than 1% of all cases. Pericardial mesothelioma has been linked to asbestos exposure. However, there is a lack of information about the exact way this mesothelioma type develops due to its rarity.
Patients with pericardial mesothelioma have a median survival of 6 months. But in recent studies, patients who received multimodal therapy have lived longer than 6 months. Treatment for pericardial mesothelioma may include:
- Chemotherapy
- Pericardiectomy surgery
- Radiation therapy
Specialists continue to explore new pericardial mesothelioma treatment options. Possible experimental treatments include photodynamic therapy and mesothelioma vaccines. Eligible patients may be able to receive these treatments through clinical trials.
Testicular Mesothelioma
Testicular mesothelioma forms in the lining around the testicle, called the tunica vaginalis. This lining covers the testes. This type is very rare, accounting for less than 1% of mesothelioma cases. This form of mesothelioma has been connected to asbestos exposure. But the exact way it develops is not fully understood.
With treatment, testicular mesothelioma has a median survival of 6 years. The most common treatment removes a testicle and its spermatic cord. Patients may also receive chemotherapy or radiation.
Resources for Mesothelioma Patients
02. Cell Types
Mesothelioma Cell Types
Mesothelioma type can be defined by cell type and tumor location. Specialists identify different cell types by their unique shapes.
Cancer cell type may affect how a patient responds to certain treatments. The three main mesothelioma cell types are:
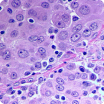
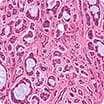
Epithelioid mesothelioma is the most common cell type, making up about 70% of cases. Epithelioid cells have box or oval shapes. They tend to respond better to treatment than other cell types. The best outcomes are associated with patients who receive both surgery and chemotherapy. Epithelioid mesothelioma survival times range from 1.5 to 6.5 years.
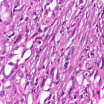
Sarcomatoid mesothelioma makes up about 10% of cases. These cells are characterized by oval or spindle shapes. Historically, prognosis for this cell type has been poorer than for others. Median survival has ranged from about 8 to 10 months with treatment. But treatment advancements are changing this.
Doctors have seen promising results treating sarcomatoid patients with immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs). ICIs are a type of immunotherapy drug that helps the body’s immune system fight cancer. In one study, survival almost doubled in pleural sarcomatoid patients treated with ICIs.
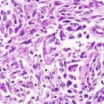
Biphasic mesothelioma, or mixed mesothelioma, accounts for about 20% of cases. Biphasic tumors contain both epithelioid and sarcomatoid cells. Median survival has ranged from about 10 to 13 months, but new cancer treatment methods may be changing this. ICI treatment has shown early promise in improving survival in pleural biphasic patients.
In addition to the three main cell types, there are also rarer mesothelioma cell types. These rare cells are often subtypes of epithelioid or sarcomatoid mesothelioma. Some defy classification.
Rare mesothelioma cell types include:
- Adenomatoid
- Benign multicystic peritoneal
- Deciduoid
- Desmoplastic
- Heterologous
- Lymphohistiocytoid
- Small cell
- Well-differentiated papillary
Treatment options may vary by type of cancer cell. Many of the rarer types have the same treatment options and similar outcomes to the more common cell types. Options may also vary by whether the mesothelioma tumor is benign or malignant.
03. Malignant vs. Benign
Malignant vs. Benign Mesothelioma
The majority of diagnosed mesothelioma cases are malignant, meaning they are cancerous. But in rare cases, mesothelioma tumors can also be non-cancerous, or benign.
Malignant tumors can grow and spread fast, which can limit treatment options. Malignant mesothelioma patients have an average life expectancy of 18 – 31 months.
Benign mesothelioma cells do not grow as aggressively. This can allow doctors to perform complete tumor removal procedures. Treatment may consist of surgery to fully remove the tumor. Benign mesothelioma generally has a good prognosis, although recurrence is possible. In rare cases, it may become malignant mesothelioma.
04. Treatment by Type
Mesothelioma Treatment by Type
Mesothelioma treatment options vary based on location and cell type. A doctor can create an individualized treatment plan based on a patient’s unique mesothelioma diagnosis. Treatment options include surgery, chemotherapy and immunotherapy. Patients may receive two or more treatments as part of a multimodal therapy plan.
Surgery
Patients eligible for aggressive mesothelioma treatment may undergo surgery. Multimodal treatment involving surgery may be the best way of extending survival. The type of surgery a patient undergoes depends on the type and location of their mesothelioma. Surgery options for the main mesothelioma types include:
- Pericardial mesothelioma: Pericardiectomy
- Peritoneal mesothelioma: Cytoreductive surgery (CRS)
- Pleural mesothelioma: Extrapleural pneumonectomy (EPP), pleurectomy decortication (P/D)
- Testicular mesothelioma: Radical orchiectomy
Currently, doctors consider cell type as a factor affecting surgery options. For example, sarcomatoid patients may not be eligible for surgery. But some experts believe this could change. They want to reexamine cell-type-based surgery qualifications in light of new immunotherapy treatments.
Immunotherapy
Different types of mesothelioma patients are increasingly likely to receive immunotherapy. The most promising mesothelioma immunotherapy uses drugs called immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs). A combination of the ICIs Opdivo® (nivolumab) and Yervoy® (ipilimumab) is approved to treat pleural mesothelioma.
Research into the use of ICIs to treat mesothelioma is ongoing. Some specialists are looking into using ICIs to treat mesothelioma in locations other than the pleura. Clinical trials are looking into treating peritoneal patients with immunotherapy.
Other specialists are looking into the potential of ICIs for fighting different cancer cell types. Early research suggests they may help sarcomatoid patients qualify for surgery. In one recent case, doctors diagnosed a patient with inoperable sarcomatoid mesothelioma. They then treated the patient with Opdivo and Yervoy. After this treatment, the patient’s condition improved enough that doctors determined the cancer was operable.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy is a common treatment for different types of mesothelioma. Doctors may treat any of the main mesothelioma types with chemotherapy. Chemotherapy may be systemic or local depending on a patient’s diagnosis and their doctor’s recommendation. It may be combined with other forms of treatment, like surgery and immunotherapy.
Patients with inoperable mesothelioma may receive systemic chemotherapy. Patients with operable pleural or peritoneal mesothelioma may be eligible for local chemotherapy. Local chemotherapy is often administered with surgery.
For example, CRS plus HIPEC is a standard peritoneal mesothelioma treatment involving surgery and localized chemotherapy. This treatment combination is associated with long-term peritoneal mesothelioma survival.
Radiation
Doctors may use radiation to treat certain types of mesothelioma. Pleural and pericardial mesothelioma patients may receive radiation. It is most often applied in a multimodal plan and seldom used alone.
Radiation is not a common treatment for peritoneal or testicular mesothelioma. It has not been tied to improved peritoneal mesothelioma survival. It is unclear whether radiation is helpful in treating testicular mesothelioma.
Palliative
Patients with any type of mesothelioma may receive palliative care. Palliative treatment is healthcare aimed at improving a patient’s quality of life at any stage of illness. For example, patients may receive fluid drainage procedures to decrease discomfort. The palliative treatment a patient receives may depend on the type of mesothelioma they have.
Mesothelioma patients may receive palliative care at any point during their cancer journey. It does not prevent patients from receiving care aimed at treating mesothelioma.
05. Common Questions
Common Questions About Mesothelioma Types
- What are the main types of mesothelioma?
The main types of mesothelioma can be categorized by location and cell type. The main location types are pleural, peritoneal, pericardial and testicular. Pleural mesothelioma is the most common location type, making up 80% – 90% of all cases. The main cell types are epithelioid, sarcomatoid and biphasic. Epithelioid mesothelioma makes up about 70% of cases.
- What is the difference between mesothelioma location and cell type?
Location and cell type refer to different mesothelioma characteristics. Location describes where the tumor is within the body, like the lining of the lungs (pleura) or lining of the abdomen (peritoneum). Cell type refers to the type of cell that the tumor is made of. Both location and cell type are important to determine prognosis and identify treatment options.
- Is mesothelioma a type of lung cancer?
Mesothelioma is not a type of lung cancer. Pleural mesothelioma forms in the lining around the lungs, called the pleura. On the other hand, lung cancer forms in the lungs. Asbestos exposure may cause mesothelioma or lung cancer, but they are not the same cancer and may be treated differently.
- What is the rarest form of mesothelioma?
According to experts, heterologous mesothelioma is the rarest form. Fewer than 60 cases have been reported in medical literature. These ultra rare tumors can contain unusual structures similar to bone and cartilage. Symptoms include breathlessness and swelling around the affected lung.