01. Mesothelioma Overview
What Is Mesothelioma Cancer?
Mesothelioma is a rare and aggressive cancer that develops in the linings of certain tissues. Pleural mesothelioma and peritoneal mesothelioma are the two most common types. The cancer is caused by exposure to a fibrous mineral called asbestos.
Inhaled and ingested asbestos fibers can lodge in internal organs and lead to tumor growth. People who experience higher levels of exposure face an elevated risk of developing asbestos diseases. But any exposure may lead to mesothelioma.
Mesothelioma Key Facts
- Pleural is the most common type of mesothelioma and makes up more than 80% of diagnoses.
- The average age at diagnosis for pleural mesothelioma is 72 years old.
- Approximately 3,000 new mesothelioma cases are diagnosed each year.
- It can take 10 – 50 years for mesothelioma symptoms to present after asbestos exposure.
For mesothelioma patients, average life expectancies range from 18 to 31 months with treatment. But there have been long-term survivors, such as Heather Von St. James. Heather is a 19-year survivor after completing a rigorous treatment plan.
Treatment often helps improve factors like quality of life and survival. Treatment plans may include traditional methods like surgery and chemotherapy or newer ones like immunotherapy. Multimodal plans, which combine different treatments, are common.
02. Symptoms
Mesothelioma Symptoms
Mesothelioma symptoms include chest and abdominal pain, fluid buildup and coughing. They can take 10 – 50 years (the latency period) to present after initial asbestos exposure. When symptoms do appear, they can easily be mistaken for less serious illnesses. The flu, pneumonia or intestinal troubles may have similar symptoms.
If you or a loved one have a history of asbestos exposure, it can be helpful to provide this information to a doctor, who can then do periodic checkups. This may help lead to an earlier diagnosis and treatment plan. With an earlier diagnosis, patients may have different treatment options. In some cases, early detection can come with an improved mesothelioma prognosis.
Common Symptoms of Malignant Mesothelioma
The amount, severity and type of mesothelioma symptoms vary for each patient. Common signs and symptoms of mesothelioma include:
- Abdominal or chest pain
- Coughing or wheezing
- Difficulty breathing (dyspnea)
- Fatigue
- Fever and night sweats
- Fluid buildup
- Loss of appetite
- Muscle weakness
- Shortness of breath
- Unexplained weight loss
Resources for Mesothelioma Patients
03. Causes
Causes of Mesothelioma
Asbestos is the only definitive cause of mesothelioma. When asbestos fibers are inhaled or ingested, they may embed in the lining of the lungs, abdomen or heart. Over time, the fibers can cause inflammation and scarring. This irritation can later lead to the development of mesothelioma cancer tumors.
How Mesothelioma Develops After Asbestos Exposure
Mesothelioma often develops decades after exposure to asbestos. It is not uncommon for someone to receive a mesothelioma diagnosis anywhere from 10 to 50 years after first being exposed to asbestos.
- Exposure: A person is exposed to asbestos fibers, which are easily inhaled or ingested.
- Embedding: The asbestos fibers become lodged in the linings of internal organs, like the lungs, abdomen and heart.
- Inflammation: Embedded fibers irritate and damage surrounding tissue.
- Cancer: Over time, tumors begin to form in the damaged tissue.
Asbestos exposure can occur in a number of ways, including:
Although high levels of exposure may increase the likelihood of the disease developing, even one-time or short-term exposure can cause mesothelioma.
04. Types
Types of Mesothelioma
There are four main types of mesothelioma, each based on the location of tumors. Prognosis, symptoms and treatment options vary between the types.
Pleural Mesothelioma
Pleural mesothelioma develops in the lining around the lungs. It is the most common type of the disease, accounting for more than 80% of all diagnoses.
Peritoneal Mesothelioma
Peritoneal mesothelioma develops in the lining of the abdomen. It is the second most common mesothelioma type, accounting for 10% – 15% of all cases.
Pericardial Mesothelioma
Pericardial mesothelioma develops in the lining around the heart. It is very rare, only accounting for 1% or less of all mesothelioma diagnoses.
Testicular Mesothelioma
Testicular mesothelioma develops in the lining of the testicles. It is the rarest type of mesothelioma and accounts for less than 1% of all cases.
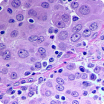
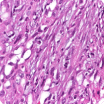
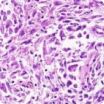
Mesothelioma Cell Types
Mesothelioma tumors can be made of different types of cells with varied properties. Patients may sometimes hear mesothelioma referred to by the cell makeup of the cancer. Below are some common mesothelioma cell types:
This is the most common mesothelioma cell type. Compared to other cell types, epithelioid mesothelioma responds well to treatment.
This cell type generally responds to immunotherapy better than chemotherapy.
The tumors contain a combination of epithelioid and sarcomatoid cells. The percentage of each cell type may affect which treatment options are available.
Recommended treatment methods vary based on mesothelioma cell type and location. Doctors can create customized treatment plans based on each individual case.
05. Diagnosis
Diagnosing Mesothelioma
It is important to diagnose malignant mesothelioma as early as possible. After recognizing symptoms, doctors confirm a mesothelioma diagnosis with a biopsy. Tissue biopsies are the only way to definitively diagnose mesothelioma.
People who know or suspect asbestos exposure can tell their doctors. A doctor can watch for signs of asbestos cancer. Those who develop symptoms can find specialists experienced in diagnosing mesothelioma.
Common Tests for Diagnosing Mesothelioma
Mesothelioma patients may receive a number of tests to help doctors reach a diagnosis. These tests may have different goals. For example, blood tests may help doctors order additional diagnostic tests. Common diagnostic tests include:
- Imaging scans: Doctors often use imaging scans like MRIs and CT scans early in the diagnostic process. These tests are still useful after a diagnosis is confirmed. For example, chest X-rays can help doctors determine the extent and location of tumors.
- Biopsies: A biopsy removes tissue or fluid for testing. It is the only way to diagnose mesothelioma. Other tests can play a role in the diagnosis process, but only biopsy testing can be conclusive.
Doctors may also order tests for other reasons. For example, a biopsy can also help determine important disease factors, like cell type. Doctors may also use testing to better understand cancer location and stage.
06. Stages
Mesothelioma Stages
After confirming a mesothelioma diagnosis, doctors often go on to estimate its stage. The most common method to determine mesothelioma stage is the tumor node metastasis (TNM) system. Mesothelioma stages range from early (stages 1 and 2) to later (stages 3 and 4).
This information helps doctors understand prognosis and treatment options. In stages 1 and 2, patients may have varied treatment options. In stages 3 and 4, the cancer has spread (metastasized). This may mean patients have different treatment options than in earlier stages.
Doctors use several factors to estimate prognosis, but an individual’s experience may differ from this estimate. Patients from stages 1 to 4 have outlived their original life expectancies. Research advances continue expanding treatment options for early- and late-stage cases.
07. Prognosis
Mesothelioma Prognosis
Prognosis is the medical expectation for how a patient’s disease will progress. A mesothelioma prognosis includes life expectancy, quality of life and other aspects of a patient’s experience. Doctors use information like stage and cell type to estimate survival time and the best treatment options for improving prognosis.
When discussing their prognosis, patients will often hear other related terms, including:
- Life expectancy: An estimate of the amount of time they will live after diagnosis. This is presented in months or years.
- Survival rate: The percentage of people in a certain group who are still alive at a specific point in time. This is typically reported in 1-, 2-, 3- or 5-year increments.
Each patient’s prognosis will vary based on many individual factors, including age and overall health. In general, treatment can help improve a patient’s prognosis. Mesothelioma specialists can create a personalized treatment plan for each patient. They can also explain what to expect during the mesothelioma treatment process.
Mesothelioma Survivors
A prognosis is a complex estimate and many factors affect it. Treatment generally helps improve prognosis. With treatment, some mesothelioma patients are able to outlive their initial life expectancy by months, years or even decades.
For example, Heather Von St. James is a pleural mesothelioma survivor of more than 19 years. During her diagnosis, doctors said she had 15 months to live. Heather had a multimodal treatment plan that included surgery and heated chemotherapy. Today, she supports mesothelioma patients and advocates for awareness of this disease.
08. Treatment
Mesothelioma Treatment Options
Treatment is the best way to help improve a mesothelioma prognosis. This can include boosting quality of life and extending life expectancy. Traditional treatments for mesothelioma include chemotherapy and surgery. Immunotherapy is a newer treatment method that has recently become standard.
These methods will often be combined to create a comprehensive treatment plan. This approach is called multimodal treatment. Multimodal plans have yielded the best known patient survival outcomes.
- Chemotherapy: Chemotherapy drugs kill cancer cells and stop them from multiplying. For mesothelioma, the standard first-line chemotherapy treatment is cisplatin or carboplatin with Alimta® (pemetrexed). It is often combined with other methods.
- Immunotherapy: Immunotherapy helps the body identify and fight cancer cells. It has been successful for patients with average or complex cases. The combo of Opdivo® (nivolumab) and Yervoy® (ipilimumab) has approval for pleural cases.
- Multimodal treatment: Multimodal treatment combines two or more cancer treatments. One common multimodal approach combines surgery and chemotherapy to remove and kill cancer cells.
- Surgery: Surgery is the method of manually removing cancerous tissue. It may be used throughout the various stages of cancer. In later stages, surgery may have a more palliative than therapeutic intent.
Patients may receive these treatments to:
- Remove tumor mass
- Kill cancer cells
- Manage side effects
- Improve quality of life
Some aspects of multimodal plans can also help manage side effects caused by treatments.
Mesothelioma cancer research continues examining emerging treatment options. Emerging methods include gene therapy, photodynamic therapy and TTFields. Patients may have access to these treatments in clinical trials.
Mesothelioma doctors can explain which clinical trials patients may qualify for. Doctors may also include emerging methods in specialized mesothelioma treatment plans.
Find Specialized Mesothelioma Treatment
For patients with mesothelioma, receiving specialized care is important. Many doctors may not have experience in treating this rare cancer. However, there are many qualified mesothelioma specialists throughout the United States.
These doctors can develop personalized cancer care plans for patients. They stay more up to date than general oncologists on the latest mesothelioma research and treatments. Mesothelioma specialists can help patients better understand and navigate their diagnosis.
Find doctors and cancer centers specializing in mesothelioma treatment near you by selecting your state below.
09. Support
Mesothelioma Support and Resources
Patients, survivors and their loved ones can find support through the mesothelioma community. For example, support groups can connect people with others who understand this disease. There are many other ways to get involved in the community or to show support.
Below are ways to connect with others about a mesothelioma diagnosis, treatment and survivorship.
10. Common Questions
Common Questions About Mesothelioma
- Is mesothelioma a form of cancer?
Malignant mesothelioma is a rare and aggressive cancer. It is caused by exposure to asbestos. When someone breathes or swallows asbestos, the fibers can embed in organs like the lungs. Over time, these fibers cause irritation and cell damage. Eventually, it may lead to cancer.
- Where does mesothelioma start?
Mesothelioma tumors start in a thin tissue called the mesothelium. This tissue is a thin protective layer covering different organs. For example, the pleura is the mesothelium that covers the lungs. The pericardium protects the heart, and the peritoneum protects organs in the belly.